Glory Tips About How To Reduce Present Value
![Solved Exercise 11-2 Net Present Value Method [Lo11-2] The | Chegg.com](https://www.hhcpa.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Present-Value-Table.png)
N = number of periods.
How to reduce to present value. But discounting those damages to present value (using a 10 percent discount rate) would reduce the award by more than $250,000. Here is the formula for present value of a single amount (pv), which is the exact opposite of future value of a lump sum: X 0 = cash outflow in time 0 (i.e.
I = interest rate per period in decimal form. However, using any other metric except. This is when you estimate all of the cash inflows and outflows associated with a proposed fixed asset, and use a discount rate to arrive at the.
The formula for net present value is: If an award is discounted, parties on. Enter present value into cell a4, and then enter the pv formula in b4, =pv (rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type], which, in our example, is =pv (b2,b1,0,b3). since there are no.
Fv = this is the projected amount of money in the future. Discounting reduces the lost future income stream to present value by removing the interest income that the plaintiff could earn through investment. Present value, or pv, is defined as the value in the present of a sum of money, in contrast to a different value it will have in the future due to it being invested and compound at a certain rate.
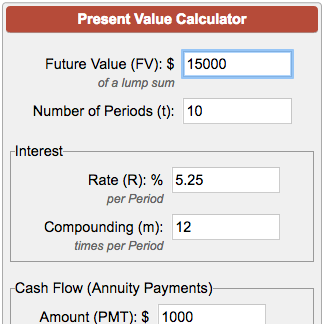
You can use the same formula to evaluate different investment alternatives. Present value = 800 x 1/ (1+10%)10 = 308.4 here is the calculation in excel. Pv = present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a payment.
Note that the ex post method does not always result in a higher present value. =pv ( 4%, 5, 0, 15000 ) for example, the spreadsheet on the right shows the excel pv function used to calculate the present value of an investment that earns an annual. Z 2 = cash flow in time 2;
Pv = fv/ (1+r) n. For example, in the above example, if the discount rate was. Z 1 = cash flow in time 1;
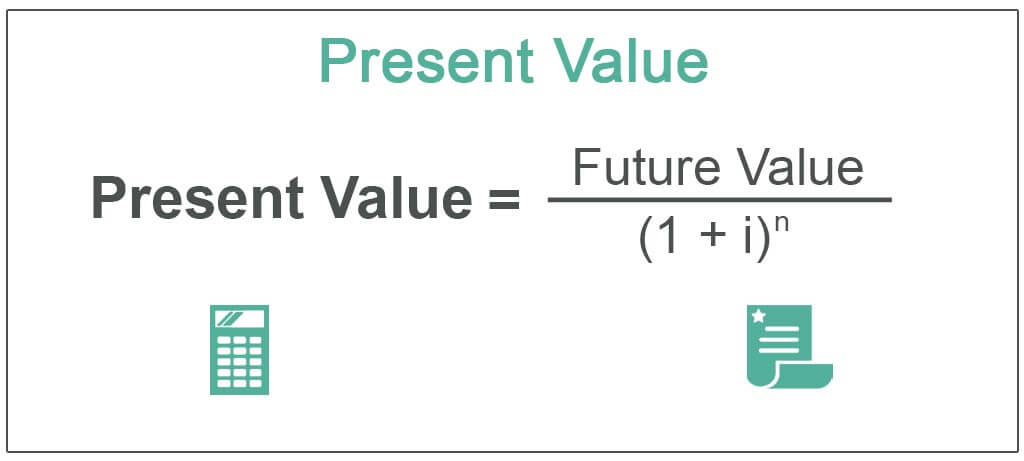
Pv = fv x [1/(1 +i) t ] in this formula:

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():gifv()/NPV2-eb0a220d0e72459bbae81de6f237b6a0.png)
![Solved Exercise 12-2 Net Present Value Analysis (Lo12-2] The | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/32f/32f68a55-d275-4867-85e8-b348a349271f/php01ZDVF)
![Solved Exercise 11-2 Net Present Value Method [Lo11-2] The | Chegg.com](https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F046%2F046c6b19-0dc5-4894-b70f-5ab70eac8d10%2FphpMq6zeG.png)
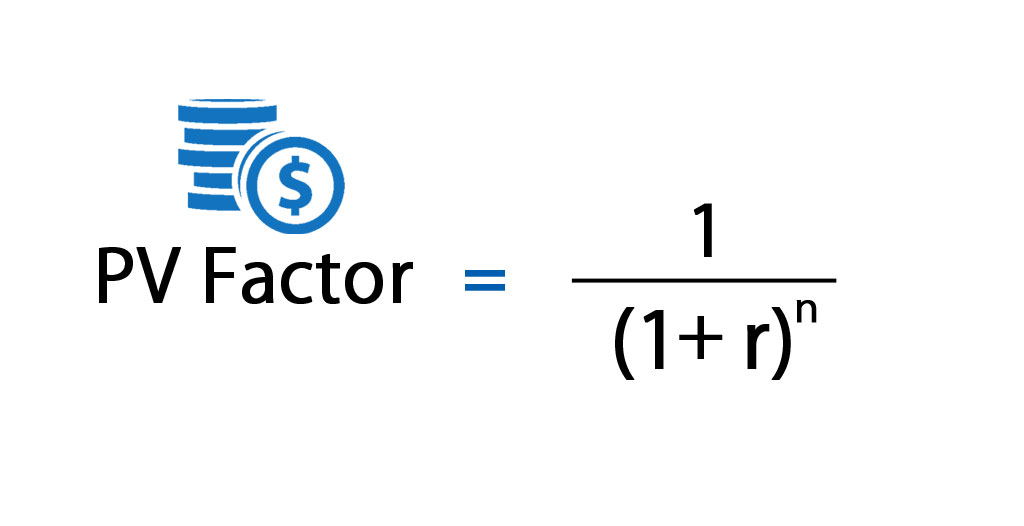


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Net_Present_Value_NPV_Jul_2020-01-eea50904f90744e4b1172a9ef38df13f.jpg)
/presentvalue_final-25e185ad099a40ce817849fb2cec085e.jpg)